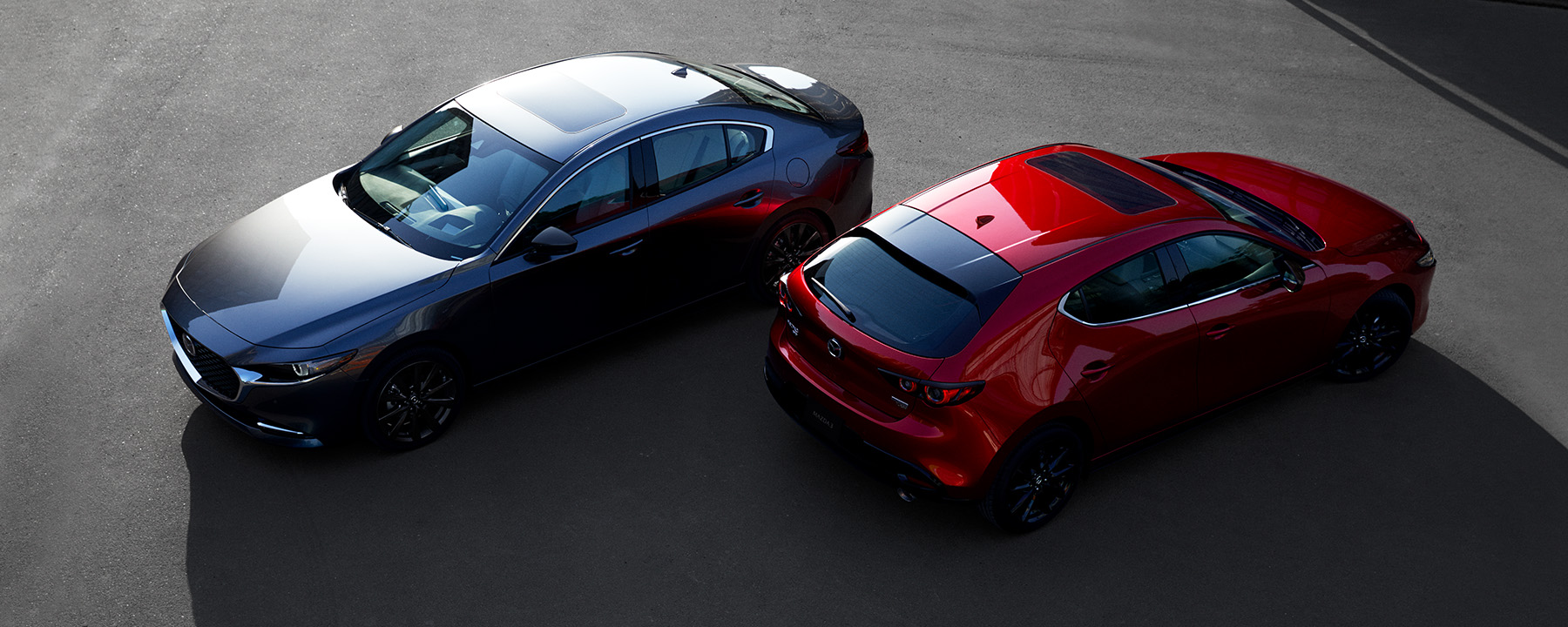
Hatchbacks vs. Sedans: What’s the Difference?
Sedans are built on a 3-box body with a separate trunk, while hatchbacks are built on a 2-box body with a connected hatch.

Hatchbacks have a rear hatch that opens to the vehicle’s interior area (2-box body), sedans have a closed-off trunk that is separated from the interior passenger area (3-box body).
The main difference between a hatchback and a sedan is the number of boxes that make up the vehicle body. Sedans are built on a 3-box body, consisting of the engine bay, interior passenger area and a separate trunk, while hatchbacks are built on a 2-box body with the engine bay and a larger interior “box” that combines the passenger area with an open cargo area behind the rear seats. Sedans also typically come as a 4-door, while hatchbacks feature 3 or 5 doors, with the hatch counting as a door.
In this article, we'll explore the differences between hatchbacks and sedans, shedding light on their benefits and potential disadvantages so that you are equipped with the information to help determine which option is best for you.

What is a sedan?
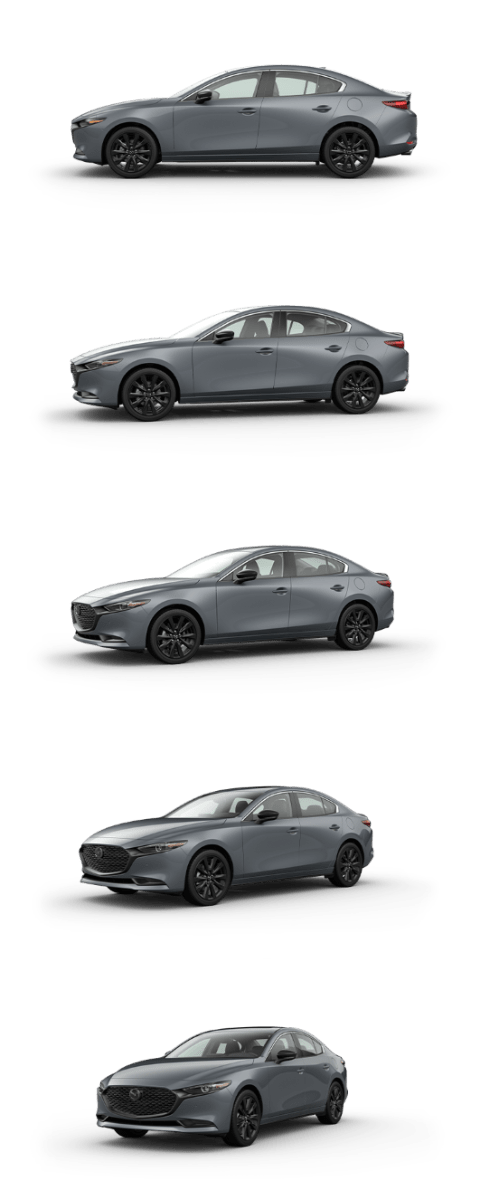
Like a hatchback, sedans (also known as “saloons” in parts of Europe) are usually designed to accommodate up to 5 passengers. However, sedans are built on a 3-box body, where one box houses the engine, the next box the passengers, and the third is for the trunk. Since the trunk is separate from the passenger area—and typically smaller than the cargo area of a hatchback—the rear roofs of sedans tend to slope lower and more dramatically toward the trunk than the roofs of hatchbacks. This can be seen in the image of the Mazda3 sedan pictured above.
Learn more about what makes a sedan a sedan in our article: ¿Qué es un sedán?
Pros and Cons
Benefits of Sedans
• The separated and enclosed trunk keeps items out of sight and protected.
• This body style offers a sleeker and more classic look.
Drawbacks of Sedans
• The fixed trunk and smaller opening may prohibit larger or irregularly shaped items from fitting.
• Sedans’ longer bodies can make parallel parking more challenging.
Learn more about what makes a sedan a sedan in our article: ¿Qué es un sedán?
 What is a hatchback?
What is a hatchback?
As mentioned above, hatchbacks are built on a 2-box body. This means that one box houses the engine, while the other box holds the passengers and the cargo area, with a hatch that opens upward. The combined passenger-cargo box is the hatchback’s defining feature and gives it the ability to hold more cargo than a similarly-sized sedan, especially if you can fold down the vehicle’s rear seats. Hatchbacks frequently seat up to 5 passengers but are usually shorter than their sedan counterparts.
Learn more about what makes a hatchback a hatchback in our article: ¿Qué es un hatchback?
Pros and Cons
Benefits of Hatchbacks
• A rear liftgate makes it easier to fit larger or awkwardly shaped items in the cargo area, particularly if the hatchback also comes equipped with foldable seats.
• Hatchbacks are often shorter and smaller than sedans, making them easier to park and maneuver.
• A larger rear window can help improve visibility when reversing or looking around.
Drawbacks of Hatchbacks
• Open cargo areas may allow more road noise into the cabin.
• Their compact size can lead to less rear passenger legroom than that found in sedans.
Learn more about what makes a hatchback a hatchback in our article: ¿Qué es un hatchback?
What is the difference between a hatchback and a sedan?
Sedans and hatchbacks are frequently lumped together because of their similar passenger capacity and size. However, as you’ve started to see, they do have key elements that make these classic car types quite distinct. Let’s take a closer look at these differences
● Cargo space: The high profile, combined passenger and cargo box, larger trunk opening and rear liftgate design of a hatchback means that this car type generally offers more cargo space and versatility than sedans.
● Headroom: Although both car styles can accommodate a similar number of passengers, hatchbacks often provide more headroom (particularly for rear passengers) due to their higher profile and less sloped roof angle.
● Legroom: Larger, full-size sedans tend to have longer body styles compared to hatchbacks, which typically offer more legroom for passengers.
● Maneuverability: This longer profile of the sedan can make it trickier to maneuver in tight urban spaces than a hatchback. However, keep in mind that sedans and hatchbacks are both considered smaller cars, especially when compared to conventional trucks and SUVs.
● Noise: Hatchbacks may have slightly more road and wind noise due to their open cargo area design. This is because passengers are seated in the same compartment as the cargo area, which is located over the rear wheels. The walled-off trunk spaces of sedans often have better noise insulation and provide a quieter cabin experience as a result.
● Availability: While hatchbacks are more popular in other parts of the world, particularly Europe, dealers in the U.S. typically keep fewer hatchbacks and trim level options in stock. Sedans will generally have more on-hand inventory compared to hatchbacks. Want to check availability? Find a Mazda dealer near you or search Mazda3 inventory.
| ATRIBUTO | HATCHBACK | SEDAN |
|---|---|---|
| ZONA DE CARGA | More space due to the combined passenger and open cargo area. | Less space because of the separate, closed trunk. |
| HEADROOM | More headroom, especially for rear passengers. | A sloped roof offers less headroom for the back seats. |
| LEGROOM | Limited rear passenger legroom. | More legroom for rear seats due to longer body (especially in full-size sedans). |
| MANEUVERABILITY | Compactness makes it easier to maneuver in tight spaces. | Less maneuverable in dense urban areas. |
| NOISE | More road and wind noise due to open cargo and passenger area. | Quieter cabin thanks to the noise insulation of the separate trunk. |
| AVAILABILITY | Less common in the U.S., so dealers usually have fewer on hand. | More readily available with a wider range of options. |
Buyer’s tip: While the above is true for more classic designs of sedans and hatchbacks, it’s also true that there are some models that blur the lines between these two car types. For example, some hatchbacks are intentionally designed with a smaller hatch, which in turn leads to a roofline that slopes in the rear like a sedan and ultimately creates less rear passenger headroom. For this reason, it’s always wise to test drive any vehicle you’re interested in and to look up the specifications of the models you’re interested in purchasing.
2024 Mazda3 2.5 Turbo Sedan Premium Plus and Mazda3 2.5 Turbo Hatchback Premium Plus shown.
Shop the Mazda3 sedans and hatchbacks
While each has their differences and advantages, choosing between a sedan and a hatchback ultimately comes down to your needs and desires for your next vehicle. Whichever your preference, Mazda has you covered.
With the Mazda3 available in both sedan y hatchback models, you can easily compare and choose which vehicle type is right for your lifestyle. Both the Mazda3 Sedan and the Mazda3 Hatchback are perfect for drivers who value sophistication and comfort and are available in multiple trims.
To experience the intuitive performance, exhilarating drive, and extensive available features of the Mazda3, see the Mazda3 in person at your local dealer o build your configuration online today.
Related Resources by Mazda
Interested in learning more about different car types and body styles?
Browse our additional articles below:
• ¿Qué es un sedán?
• ¿Qué es un hatchback?
• What is a CUV?
• What is an SUV?
• Sedans vs. SUVs
• Crossovers vs. SUVs
Este artículo está previsto para fines informativos generales únicamente y se basa en la última información de la competencia disponible al momento de la publicación. La información incluida aquí está sujeta a cambios sin previo aviso y no impone obligación alguna a Mazda. Revisa diversos recursos antes de tomar una decisión de compra. Visita el centro de recursos para leer más artículos.